Soil deficiencies can greatly affect the growth and health of plants, leading to visible physical signs that can help gardeners and farmers identify and correct the problem. Here are some of the major soil deficiencies and the physical signs they cause in plants, as well as fertilizer recommendations for correcting the defect:
Signs Of Soil Nutrient Deficiency And Correction
1. Nitrogen Deficiency:

Nitrogen is an essential element for plant growth, as it helps with the development of leaves and stems. A nitrogen deficiency can cause yellowing of the leaves, stunted growth, and a lack of vigor in the plant. To correct this deficiency, use fertilizers that are high in nitrogen, such as ammonium nitrate or urea.
Read Also: How To Do Soil Test For Your Farmland [Laboratory And Home Kits Guide]


Read Also: Crop Rotation for Disease Prevention in South Africa
2. Phosphorus Deficiency:

Phosphorus is important for root growth, flower and fruit development, and energy transfer within the plant. A phosphorus deficiency can cause a purpling of the leaves, stunted growth, and poor fruit production. To correct this deficiency, use fertilizers that are high in phosphorus, such as bone meal or rock phosphate.

3. Potassium Deficiency:

Potassium is important for water regulation, disease resistance, and overall plant health. A potassium deficiency can cause yellowing of the leaves, wilting, and poor fruit production. To correct this deficiency, use fertilizers that are high in potassium, such as potassium chloride or potassium sulfate.
Read Also: Cost-Effective Soil Testing Method [No Home Soil Kit & Lab Test]

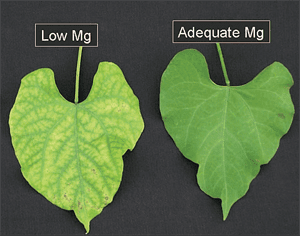
4. Magnesium Deficiency:

Magnesium is essential for photosynthesis and the formation of chlorophyll. A magnesium deficiency can cause yellowing of the leaves, particularly between the veins, and a lack of vigor in the plant. To correct this deficiency, use fertilizers that are high in magnesium, such as dolomitic lime or Epsom salt.
Read Also: How To Test Soil Acidity Without Lab or Kit
5. Calcium Deficiency:

Calcium is important for cell division and growth, and the development of strong roots and stems. A calcium deficiency can cause stunted growth and poor fruit production. To correct this deficiency, use fertilizers that are high in calcium, such as lime or gypsum.

6. Zinc Deficiency:
Zinc deficiency in plants causes stunted growth and yellowing of the leaves. It can also lead to delayed flowering and reduced yields. The best fertilizer to fix zinc deficiency is a fertilizer that contains zinc sulfate.
7. Iron Deficiency:
Iron deficiency in plants causes yellowing of the leaves (chlorosis) and stunted growth. It can also lead to reduced yields. The best fertilizer to fix iron deficiency is a fertilizer that contains iron sulfate.
What causes nutrient deficiency in soil?
Nutrient deficiency in soil can be caused by a number of factors, including:
- Poor soil fertility:
This can be caused by a lack of essential nutrients in the soil, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, or by an imbalance of the nutrients present in the soil.
- Overgrazing:
Overgrazing can lead to a depletion of organic matter in the soil, which can reduce the availability of nutrients in the soil.
- Poor soil management:
Poor soil management practices, such as tillage that breaks down soil structure, can lead to soil compaction and reduce the availability of nutrients in the soil.
- Improper irrigation:
Improper irrigation can lead to waterlogged or dry soil, which can reduce the availability of nutrients in the soil.
- Soil contamination:
Contamination of soil with toxic substances, such as heavy metals or industrial chemicals, can reduce the availability of essential nutrients in the soil.
Conclusion
It is important to note that soil testing is always recommended before applying fertilizer to your plants. This will give a more accurate picture of what your soil needs. Additionally, it is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions when applying any fertilizer and to use it in the recommended quantity. Over-fertilization can cause damage to the plants



