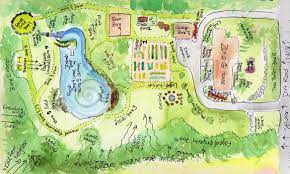
Permaculture design is a way of looking at the natural world, and designing landscapes, cities, and farms in ways that are in harmony with nature. It is an all-inclusive approach to planning and managing land and resources, based on the principles of ecology, sustainability, and self-sufficiency.
Permaculture design aims to create systems that are ecologically sound, economically viable, and socially just. Permaculture is based on a general approach to land management, taking into account the physical, social, economic, and spiritual aspects of the land and its inhabitants.
Permaculture design incorporates natural cycles, energy conservation, and the use of appropriate technologies to create a sustainable system of food production, land management, and community building.
If you have little or no knowledge about permaculture design, this is the best material for you. So, make sure you read through to the end to learn all that you need to know.
What is Permaculture Design? [Full Beginner Guide]
Permaculture design refers to the ecological design system which seeks to create resilient, self-sustaining, and regenerative systems of food production and land management. Permaculture is based on principles of ecology, biology, and systems thinking and are applied to the design of sustainable human settlements and agricultural systems.
Interestingly, permaculture design can be used to create a wide variety of systems, from urban gardens to large-scale farms, and can be applied to any environment or situation.
However, there are important factors you need to know when embarking on permaculture design so that you can judiciously practice permaculture within its intended scope. These are:
-
Understand the Principles of Permaculture Design
Permaculture design is an ecological approach to land management, using patterns found in nature to design sustainable human settlements and agricultural systems. It is based on the principles of Earth Care, People Care, and Fair Share.
- Earth Care: Permaculture design is rooted in the idea that we must take care of our natural environment to sustain ourselves. This means implementing strategies that protect soil, air, and water quality, conserve resources, and promote biodiversity.
- People Care: Permaculture design recognizes the importance of human communities and acknowledges that our well-being is dependent on the well-being of others. This includes providing support and resources to vulnerable populations, promoting social justice, and creating equitable access to resources.
- Fair Share: Permaculture design also encourages us to be mindful of our consumption, emphasizing the need to limit our use of resources and share the abundance of what we have. This includes reducing our waste, reusing and recycling materials, and practicing sustainable agriculture.
By following these principles, permaculture design can help you create sustainable and regenerative systems that benefit both people and the planet.
-
Learn the Basics of Permaculture Design
Once you understand the principles of permaculture design, you can start to learn the basics. Permaculture design utilizes several techniques, such as agroforestry, permaculture zones, natural building, and aquaculture. You can learn more about these techniques, and how to apply them to your projects, by taking a permaculture design course.
-
Create a Design
Once you have a basic understanding of permaculture design, you can start to create your design. Start by making a site map of your land, taking note of the sun, wind, water, and soil conditions. Then, begin to brainstorm ideas for how you can incorporate permaculture principles into your design.
-
Plant and Implement Your Design
Once you have a design, it’s time to start planting and implementing your design. Start with the easiest projects first, such as building soil, planting trees, and establishing water catchment systems. As your design evolves, you can add more complex elements, such as setting up a compost system, planting a food forest, and creating renewable energy systems.
-
Monitor and Maintain Your Design
Permaculture design is an ongoing process. As the environment changes, you will need to adjust your design accordingly. As you maintain your design, pay attention to what is working, and what needs to be changed.
Permaculture design is an exciting, rewarding, and holistic way to work with the land. Once you understand the principles and basics of permaculture design, you can start to create your own sustainable, self-sufficient system. With patience, dedication, and a little creativity, you can create a design that will last for generations.
Permaculture Design Guide
Permaculture is an ecological design system that utilizes natural elements and principles to create sustainable and self-sufficient human habitats. It is a holistic approach to living that seeks to create symbiotic relationships between human settlements and their natural environment. Permaculture is based on the principles of observation, design, maintenance, and resilience.
Permaculture is not a single set of rules but a set of guidelines that can be applied in various ways depending on the needs of the individual or group. It is an ever-evolving system, and each permaculture practitioner brings their unique knowledge and experience to the process. This article will provide an overview of the fundamental guidelines of permaculture.
Observation
Permaculture begins with observation. You will have to observe the land, climate, and environment all of which are key to understanding how to best design and utilize the space. Observing the land is essential to understanding what types of plants, animals, and other organisms live in the area.
It also helps you to identify potential natural resources such as water and wind. All of these factors help to determine the most appropriate design and management strategies.
Design
Design is an integral part of permaculture. It is the process of putting together the elements of a system to create a harmonious, sustainable, and productive environment. Designing a permaculture system requires an understanding of the land, climate, and other environmental factors.
It also requires an understanding of the needs of the people and other organisms that will occupy the space.
Maintenance
Maintenance is essential to keeping a permaculture system functioning. This includes managing the plants and animals that live in the system, monitoring water resources and soil fertility, and controlling pests. Maintenance also involves the continuous assessment of the system to ensure that the desired outcomes are being achieved.
Resilience
Resilience is the ability of a system to adjust and adapt to changing conditions. Permaculture systems are designed to be resilient, meaning they can withstand extreme weather and other disturbances without significant damage. Resilience is achieved through careful design, maintenance, and observation.
Permaculture Implementation
Permaculture implementation comes up immediately after you have completed your design.
The first step in the implementation of permaculture design is to observe and analyze the environment. This allows you to identify the key elements in the system, such as topography, soil type, water sources, wildlife, and human influences.
You can then use this information to develop a plan that takes into account the needs of the environment, its inhabitants, and any other stakeholders.
Once the plan is in place, you can begin to implement it through the use of various strategies, such as agroforestry, natural water management, soil building, and renewable energy systems.
These strategies can be used individually or in combination to create a robust and resilient system. You should also consider potential risks and resource limitations, as well as the potential for long-term success.
In addition to the physical implementation of the design, permaculture also involves taking a holistic approach to the management of the system. This includes monitoring and evaluating the progress of the design, as well as engaging with the local community and other stakeholders to ensure that the design meets their needs and is sustainable in the long term.
What is Permaculture Farming
Permaculture farming is an ecological farming system that uses principles of sustainability, biodiversity, and self-sufficiency to create a comprehensive, self-sustaining farming system. Permaculture farming relies on natural systems, such as the integration of plants, animals, and soil, to create a balanced, healthy, and productive ecosystem.
Permaculture farms are based on the principle of providing maximum yields with minimum input. This is achieved by creating a closed-loop system, with the use of natural resources and practices such as composting, crop rotation, and companion planting. Permaculture farms also strive to reduce or eliminate the use of synthetic chemicals and fertilizers.
Permaculture farming is not only beneficial for the environment, but it can also be beneficial for the farmer. By utilizing sustainable practices and natural resources, permaculture farming can significantly reduce costs associated with chemical fertilizers, pesticides, and other inputs.
Additionally, permaculture farms often yield higher quality and more diverse crops, due to the increased diversity of the farm’s ecosystem.
Permaculture farming is becoming increasingly popular, as it offers an alternative to traditional farming methods which can be more environmentally damaging. It is a great way to reduce environmental impact, while still producing high-quality
Permaculture Design Course
A Permaculture Design Course (PDC) is a comprehensive, hands-on educational experience that provides practical information and skills for creating sustainable human habitats. The goal of a PDC is to teach participants how to design, implement and maintain permaculture systems that are ecologically sound, economically viable, and socially just.
The PDC typically consists of a series of lectures, group discussions, and practical exercises that cover a variety of topics, including:
- Introduction to Permaculture and Overview of the Principles
- Natural Patterns and Design Processes
- Soil Fertility, Water Management, and Climate Strategies
- Appropriate Technology and Energy Conservation
- Agroforestry and Food Production
- Natural Buildings and Structures
- Animal Care and Husbandry
- Conservation and Restoration
- Social and Economic Strategies
- Community Development
The PDC also includes field trips and design projects that allow participants to apply what they have learned in a real-world setting.
Upon completion of the course, students should have a comprehensive understanding of permaculture principles and the ability to design, implement and maintain successful permaculture systems.
Permaculture Ideas
Here are a few permaculture Ideas that you can venture start.
No-Dig Mulch Gardens
No-dig mulch gardens are an important part of permaculture, as they allow you to create a low-maintenance and productive garden without needing to dig the soil. No-dig mulch gardens are a great way to practice permaculture, as they help to conserve soil, water, and energy.
In a no-dig mulch garden, you create a layer of organic mulch over the top of the soil. This layer of mulch helps to retain moisture, prevent weeds, and add organic matter to the soil.
This type of garden is ideal for creating a low-maintenance and productive garden without having to till the soil, thus preserving the soil structure and preventing compaction. It can also be a great way to create a garden on a slope or in a small space.
They also promote biodiversity, as the organic mulch provides nutrients for beneficial organisms, such as earthworms and mycorrhizal fungi, which help to break down organic matter and build soil structure. Additionally, no-dig mulch gardens can be used to create a no-till system, which helps to keep carbon in the soil and reduce the release of greenhouse gases.
Living Roof
Living roofs, also known as green roofs, are an important aspect of permaculture. Living roofs provide many advantages including improved air quality, increased insulation for buildings, and reduced water runoff.
Living roofs are made up of a substrate that is covered with soil, vegetation, and sometimes other materials. The plants can include grasses, herbs, shrubs, and trees, depending on the size and scope of the living roof.
Living roofs can provide many benefits to the environment and people. They help reduce air pollution, increase insulation for buildings, reduce energy costs by keeping interior temperatures more stable, and many more.
Reusing Tyres
Reusing tyres in permaculture is a great way to repurpose waste and create a useful and aesthetically pleasing garden feature. Tyres can be used as raised beds, creating a great space for growing vegetables, herbs, and flowers.
They provide insulation for the soil and can be used to grow plants in even the most difficult of soils. They also can be used to create a unique garden feature. For example, tyres can be filled with soil, stones, and plants and stacked to create a retaining wall or used to create a terraced garden.
Tyres can also be used as planters. They can be filled with soil and used to grow vegetables, herbs, and flowers. They can be used to create vertical gardens, hanging gardens, and even window boxes.
Tyres can also be used to create ponds. They can be filled with water and used to create a beautiful water feature in the garden. They can also be used to create a bog garden by filling them with soil and placing aquatic plants in them.
Swales
Swales are an important feature of permaculture design, providing a variety of beneficial functions. A swale is an earthen ditch dug into the landscape, often lined with logs, rock, or other soil reinforcements.
Swales can be used to capture and store rainwater, slow runoff, reduce erosion, increase soil fertility, and create habitat for wildlife. Swales can also be used to create contour lines on slopes, reducing the need for terracing.
When planted with trees, swales can sequester carbon, create shade, and provide sources of food and habitat. Swales can be an integral part of a permaculture design, helping to create a self-sustaining system that is resilient to environmental challenges.
Forest Gardens
A forest garden is a type of garden that is inspired by the structure and function of natural forest ecosystems. It is a permaculture-based system of polyculture that utilizes companion planting, companion animals, and other strategies to create an aesthetically pleasing, low-maintenance food production system that mimics the diversity and resilience of a natural forest.
Forest gardens are designed to produce an abundance of food and non-food products while also providing a habitat for wildlife. Forest gardens can be designed to mimic any climate and soil type and can include a variety of different trees, shrubs, and perennials.
Edible Balconies
Edible balconies are a great way to incorporate permaculture principles into your outdoor space. Edible balconies are ideal for those looking to grow their food and create an attractive and productive outdoor space.
When creating an edible balcony, it’s important to consider the local climate, soil, and access to water. Choose plants that are well-suited to your environment and will thrive in your space.
Think about creating a self-sustaining system that utilizes natural resources such as rainwater and compost. Consider adding a water-harvesting system and compost bins to your balcony.
Herbs and vegetables are ideal for balconies, though you can also add fruit trees, vines, and shrubs. Choose native plants that will attract beneficial insects and birds. Many edible plants can also be used as ornamentals, adding to the beauty of your balcony. To maximize your space, consider vertical gardening techniques such as hanging baskets and wall planters.
Water Harvesting
Water harvesting is an important part of permaculture, a system of agricultural and environmental design. Water harvesting is a way to capture, store and use rainwater for agriculture and other uses.
Water harvesting techniques have been used in many cultures for thousands of years. In permaculture, water harvesting can be used to create productive and efficient gardens, farms, and landscapes.
Water harvesting techniques can range from simple rain barrels to complex systems that utilize terraces, swales, ponds, or other design elements.
Permaculture PDF
Permaculture PDF contains easy-to-follow information with detailed plans for establishing a permaculture garden, including design considerations, soil testing & preparation, gardening techniques, and start-up tips.
Permaculture is a design system that can be applied to any situation and may even be the best solution. Permaculture PDF will help you recognize ways in which permaculture systems are already working so that you can take advantage of them as opportunities present themselves around you.
Permaculture Design Patterns
Permaculture design patterns use nature as a model to create sustainable, regenerative, and productive systems. These patterns are based on the concept of working with nature, not against it and creating systems that are self-sustaining and low-maintenance.
The patterns are based on a few core principles, such as working with natural processes, designing for resilience, and emphasizing diversity, which is then applied to different aspects of a permaculture system, such as soil building, water management, plant selection, and energy efficiency.
Permaculture design patterns also focus on creating a balance between humans and nature. These patterns are designed to create a mutually beneficial relationship between people and their environment by incorporating natural elements into the design.
For example, a permaculture design pattern may focus on creating a balance between water sources, soil fertility, and wildlife habitats.
By using permaculture design patterns, people can create a more sustainable and regenerative way of living that is both beneficial to the environment and people. These patterns are an important part of the permaculture movement, and they can help us create a more sustainable and resilient future.
Permaculture Design Ideas
Below are 10 permaculture design ideas that you can implement on your farmland.
Edible Landscaping
Incorporate edible plants into your landscape design for multi-functional use. Trees, shrubs, and perennials can provide food as well as visual interest and beauty.
Water Conservation
Utilize rainwater catchment systems, swales, and berms to capture, store, and redistribute rainwater and runoff to areas in need of water.
Food Forests
Plant guilds of food-producing trees, shrubs, perennials, and annuals in a layered, interdependent system that mimics natural forest ecosystems.
Aquaculture
Incorporate ponds, swales, and other water features into your design to create an aquatic ecosystem that provides food, wildlife habitat, and aesthetic beauty.
Composting and Soil Building
Use composting and other soil-building techniques to improve soil fertility and to help create a healthy, living soil that is capable of sustaining a variety of plants and animals.
Perennial Polycultures
Design a system of interdependent plants that can grow together to provide food, habitat for wildlife, and other benefits.
Natural Building
Use natural and recycled materials to build structures that are in harmony with the environment and promote sustainable living.
Natural Pest Control
Incorporate companion planting, beneficial insects, and other natural pest control methods to reduce the need for synthetic pesticides.
Renewable Energy Sources
Implement solar, wind, and other renewable energy sources to reduce dependence on non-renewable energy sources.
Eco-Village Design
Design an intentional community that is focused on living in harmony with the environment, sharing resources, and exchanging knowledge.
Permaculture Design Rules
The Permaculture ethic is based on five main principles:
- Observe and Interact: Take time to observe and get to know the land and its inhabitants, both human and animal, before making any changes.
- Catch and Store Energy: Make use of renewable resources such as sunlight and water to create a sustainable and self-sufficient system.
- Obtain a Yield: Produce food, fuel, and other resources while minimizing waste and pollution.
- Apply Self-Regulation and Accept Feedback: Balance inputs and outputs to maintain a sustainable system. Be open to feedback from the environment to inform your decisions.
- Use and Value Renewable Resources and Services: Utilize renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, to power your system.
- Produce No Waste: Design your system to produce as little waste as possible and recycle any waste that is produced.
- Design from Patterns to Details: Begin with general patterns, such as the sun’s movement and the water cycle, and then move to the specifics.
- Integrate Rather than Segregate: Combine elements of your system that serve multiple functions to create a more efficient and productive system.
- Use Small and Slow Solutions
- Design ecosystems that mimic nature’s ways of working,
- Build structures with modular parts which can be assembled as needed,
- Design tools that are easily made and repeatedly used
Permaculture Garden Plan
Here are a few garden plan tips that will be beneficial to you.
Planting a Diverse Variety of Edible and Medicinal Plants
Planting a variety of edible and medicinal plants that can thrive in your climate is a great way to start a permaculture garden. Not only will this create a habitat for beneficial insects and animals, but it will also provide you with nutritious and medicinal foods.
Use Companion Planting
Making use of companion planting is a great way to increase the yield of your permaculture garden. Planting beneficial plants near one another can help to increase pollination, reduce pests, and provide protection from harsh weather.
Maximize Water Efficiency
Water is a precious resource, and permaculture gardens should be designed to maximize water efficiency. Utilize swales and other water-harvesting techniques to capture and store rainwater. Plant water-wise plants and create mulch layers to reduce evaporation.
Create a Polyculture
Polyculture is the practice of planting a variety of plants in the same space. This not only creates a diverse habitat but also reduces the need for fertilizers and pesticides. Planting a polyculture is a great way to create a sustainable and resilient permaculture garden.
Incorporate Animal Husbandry
Animal husbandry is an important part of permaculture. Raising animals such as chickens, rabbits, and goats can provide you with eggs, milk, and meat while reducing the need for fertilizers and pesticides. Animals also help to spread seeds and increase biodiversity.
Permaculture Design Principles
Permaculture design is based on 12 core principles, which are the foundation of all permaculture projects. These principles are:
- Observe and Interact: Get to know the land, the climate, and the creatures that inhabit it before making any decisions.
- Catch and Store Energy: Harness natural energy sources and use them to power homes and businesses.
- Obtain a Yield: Design systems that produce useful products and services.
- Apply Self-Regulation and Accept Feedback: Pay attention to how your actions affect the environment, and use feedback to adjust your systems accordingly.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0mwRAf3z9ag
- Use and Value Renewable Resources and Services: Utilize renewable resources such as solar, wind, and water to meet your needs.
- Produce No Waste: Design systems that produce no waste.
- Design from Patterns to Details: Start with the big picture and work your way down to the details.
- Integrate Rather than Segregate: Design systems that are integrated and self-sustaining.
- Use Small and Slow Solutions: Implement small, incremental changes that will have long-term effects.
- Use and Value Diversity: Encourage and nurture biodiversity in your systems.
- Use Edges and Value the Marginal: Pay attention to the edges of your systems, as they often produce unexpected and valuable outcomes.
- Creatively Use and Respond to Change: Be prepared to adjust your systems as the environment changes.
Benefits of Permaculture Design
Permaculture design offers significant benefits, including:
- Reducing the amount of energy, water, and other resources used in food production, by using natural ecosystems and cycles.
- Promoting biodiversity and creating habitats for wildlife.
- Increasing soil fertility and providing better food security.
- Reducing the amount of waste generated, conserving resources, and reducing pollution.
- Enhancing the aesthetic beauty of an area.
- Creating a more harmonious relationship between people and the environment.
- Producing healthy, sustainable, and high-quality food.
- Supporting local economies and providing income-generating opportunities for people.
- Offering educational opportunities for people of all ages.
- Creating social networks and strengthening community ties.
Permaculture Design Software
Permaculture design software is an important tool for permaculture practitioners. It allows you to create and visualize a permaculture landscape design, prioritize and track tasks and resources, and analyze the impacts of different design scenarios.
By using permaculture design software, you can create a comprehensive design that incorporates a variety of permaculture principles, such as water conservation, soil management, crop rotation, and energy efficiency.
The software can also provide you with the ability to create detailed reports, analyze data, and compare different design scenarios. Permaculture design software can be used by both professionals and hobbyists to create a beautiful and sustainable permaculture landscape.
Example of permaculture software includes
- Evernote
- Gardenate
- Maps 3D
- Plantsnap
- Sun Seeker
- Theodolite
- Windy
Conclusion
Permaculture design is simply designed, low-maintenance gardens that are ecologically sound and sustainably productive. It creates agricultural systems which sustain the environment by protecting it from erosion, reducing pollution, providing sustainable soil building, and recycling nutrients.
Permaculture designs are both simple and easily adapted in application to any ecosystem or region. This guide helps you identify species that will help achieve goals such as creating healthy bio-diverse ecosystems, saving water and energy, and much more.